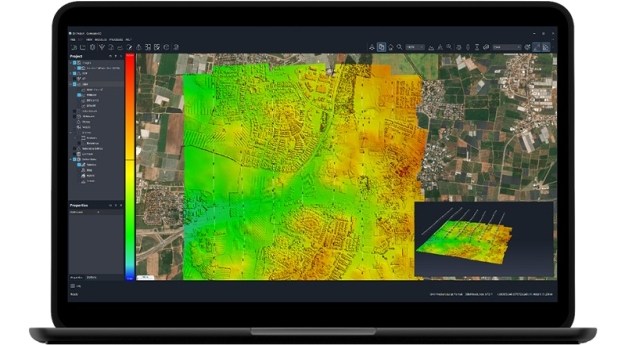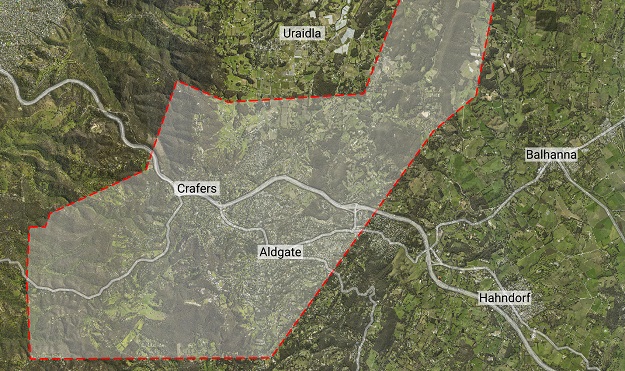
Aerometrex’s LiDAR survey encompassed 6,300 dwellings and other structures within an 80-square-kilometre area in the Adelaide hills. Images courtesy Aerometrex.
Using airborne LiDAR during the recent summer months, Aerometrex carried out a detailed survey of the bushfire fuel loads across some of the most densely populated, high risk areas of the Adelaide Hills, including Stirling, Aldgate and Bridgewater.
The company says this is the first time this work has been done in Australia, and it hopes the datasets will provide critical information to the South Australian Government and Country Fire Service (CFS) that will aid both agencies in generating informed response plans to future bushfires, as well as helping them gain a better understanding of the current risk to lives and infrastructure in the region.
It should also help in developing targetted bushfire fuel load management plans to prepare throughout the year and facilitate community communication to enable fuel management on private land and foster higher bushfire risk awareness.
The survey analysed more than 6,000 dwellings and structures across 80 square kilometres. Among other results, the company found close to one-third of the properties have high fuel loads in their proximity (within 100 m), with the average distance by road to the nearest bushfire ‘last resort refuge’ found to be 7.5 kilometres.
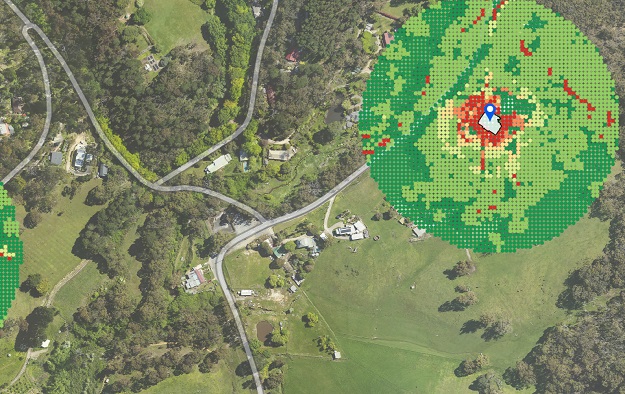
Remotely generated indicative bushfire attack level (BAL) assessments for two properties in the Adelaide hills. BAL measures the severity of the potential exposure to ember attack, radiant heat and direct flame contact. BAL is used to establish construction requirements to improve protection from bushfire attack.
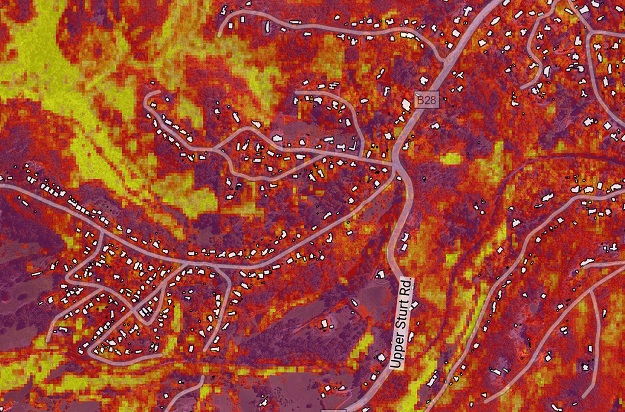
This elevated fuel load density map shows the amount of fuel between 70 cm and 1.0 m above ground. It can be used to identify areas for targetted fuel load reduction activities.
The project builds upon foundational research completed by the company in 2020 that intrinsically linked standardised visual and physical fuel load measurements collected in the field by Fire Management Officers with measurements taken from an aircraft using LiDAR.
The results of the survey include a range of maps that correlate closely with overall fuel hazard, including cumulative fuel load density and fuel load vertical connectivity, as well as the amount of physical fuel load across the landscape, in tonnes per hectare.
In addition, Aerometrex has developed a new automated methodology to provide bushfire experts with a remotely calculated Bushfire Attack Level for any existing structure, or proposed new structure, within the survey area.
Aerometrex hopes to collaborate closely with the South Australian Government, CFS and leading bushfire industry experts in the coming months to maximise the benefits of these datasets to the community.
The project is the first step towards using Airborne LIDAR to analyse bushfire fuel load for different vegetation types in other states and territories.
Stay up to date by getting stories like this delivered to your inbox.
Sign up to receive our free weekly Spatial Source newsletter.